[ad_1]
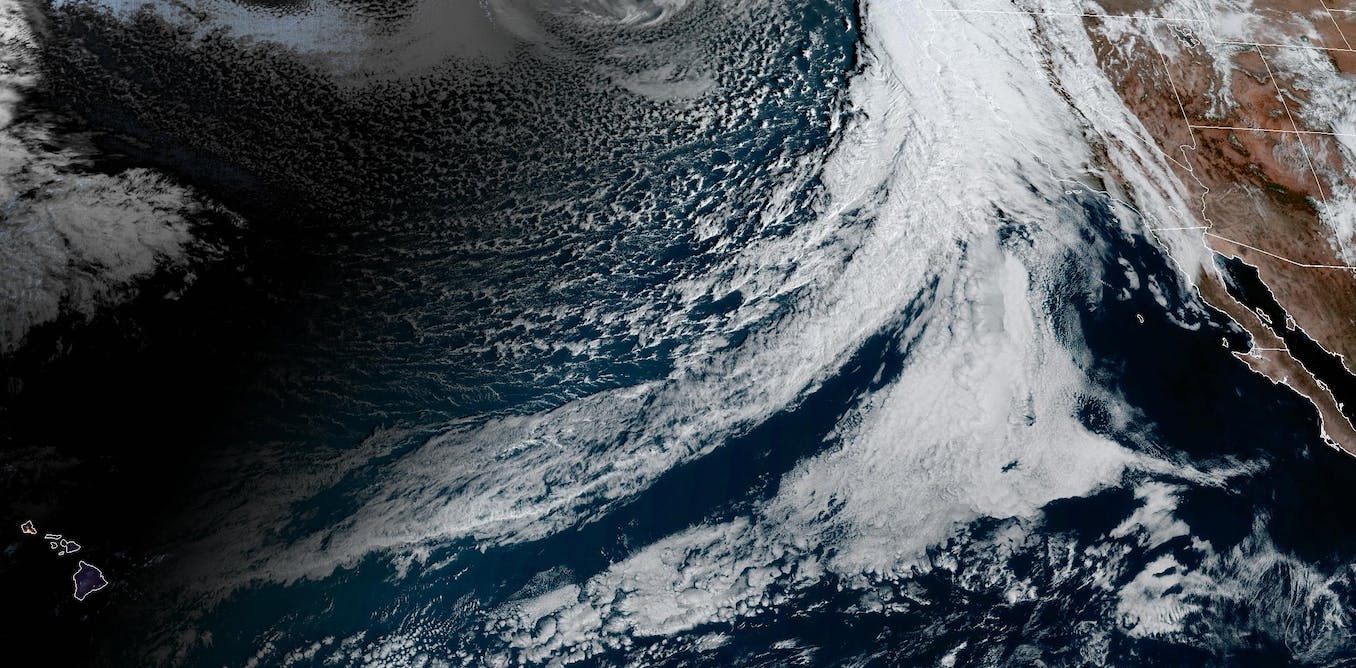
Tens of millions of individuals have been under flood alerts and winter storm warnings on Jan. 31 and Feb. 1, 2024, as a series of atmospheric rivers introduced heavy downpours and the specter of flooding, mudslides and avalanches to the Pacific Northwest and California. One other highly effective storm was anticipated just a few days later.
Whereas these storms are dreaded for the injury they’ll trigger, they’re additionally important to the area’s water provide, significantly in California, as Qian Cao, a hydrologist on the College of California, San Diego, explains.
What are atmospheric rivers?
An atmospheric river is a slim hall or filament of concentrated water vapor transported within the environment. It’s like a river within the sky that may be 1,000 miles long. On common, atmospheric rivers have about twice the regular flow of the Amazon River.
When atmospheric rivers run up in opposition to mountains or run into native atmospheric dynamics and are pressured to ascend, the moisture they carry cools and condenses, to allow them to produce intense rainfall or snowfall.
Atmospheric rivers happen everywhere in the world, mostly within the mid-latitudes. They type when large-scale climate patterns align to create slim channels, or filaments, of intense moisture transport. These begin over heat water, sometimes tropical oceans, and are guided towards the coast by low-level jet streams forward of chilly fronts of extratropical cyclones.
Alongside the U.S. West Coast, the Pacific Ocean serves because the reservoir of moisture for the storm, and the mountain ranges act as limitations, which is why the western sides of the coastal ranges and Sierra Nevada see a lot rain and snow.
Why are back-to-back atmospheric rivers a excessive flood danger?
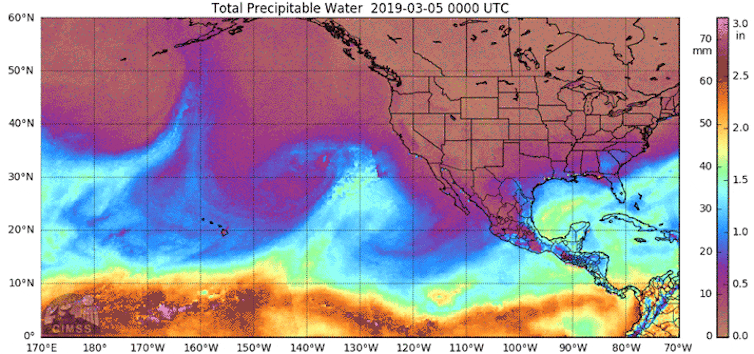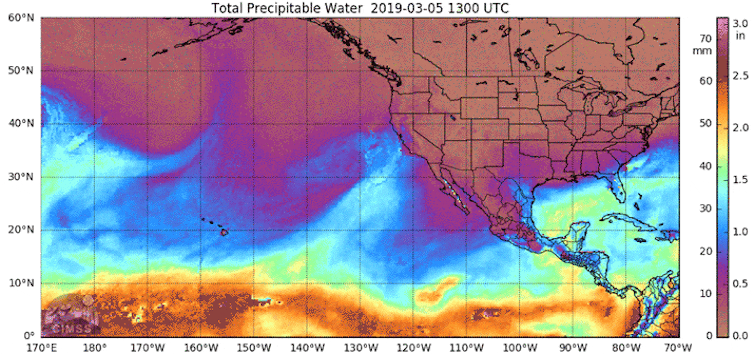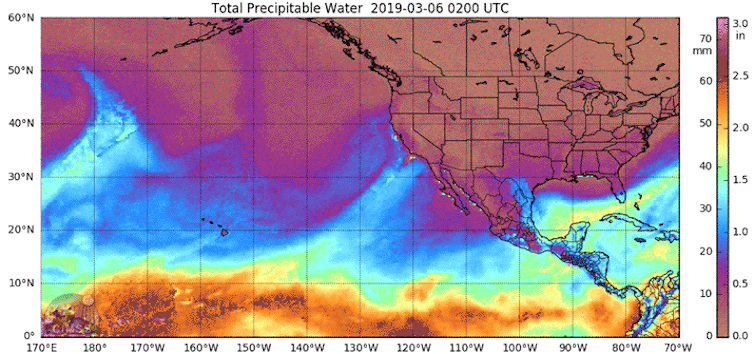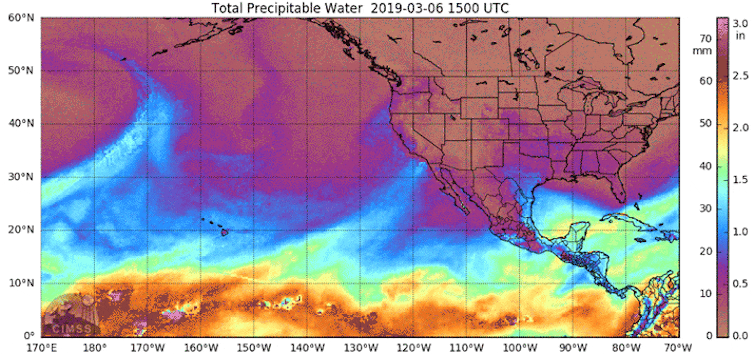
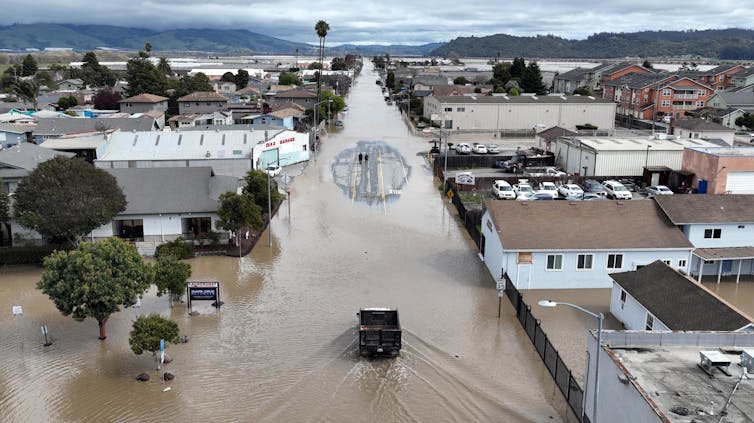
Consecutive atmospheric rivers, generally known as AR households, can cause significant flooding.
The primary heavy downpours saturate the bottom. As consecutive storms arrive, their precipitation falls on soil that may’t take up extra water. That contributes to extra runoff. Rivers and streams refill. Within the meantime, there could also be snowmelt as a result of heat temperatures, additional including to the runoff and flood danger.
California skilled a historic run of 9 consecutive atmospheric rivers within the span of three weeks in December 2022 and January 2023. The storms helped bring most reservoirs back to historic averages in 2023 after a number of drought years, however additionally they produced damaging floods and debris flows.
NOAA
The reason for AR households is an energetic space of analysis. In contrast with single atmospheric river occasions, AR households are typically related to decrease atmospheric strain heights throughout the North Pacific, greater strain heights over the subtropics, a stronger and extra zonally elongated jet stream and hotter tropical air temperatures.
Giant-scale climate patterns and local weather phenomena such because the Madden-Julian Oscillation, or MJO, also play an important role within the era of AR households. An energetic MJO shift occurred in the course of the early 2023 occasions, tilting the percentages towards elevated atmospheric river exercise over California.

Josh Edelson/AFP via Getty Images
A current research by scientists at Stanford and the College of Florida discovered that storms inside AR households cause three to four times more economic damage when the storms arrive again to again than they’d have attributable to themselves.
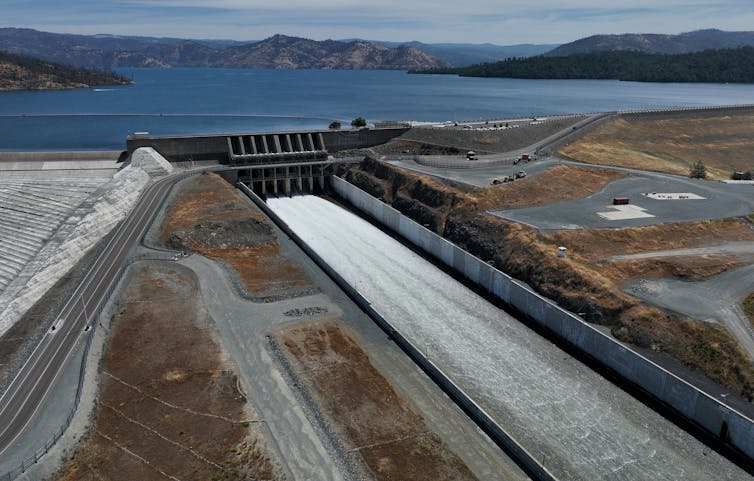
How essential are atmospheric rivers to the West Coast’s water provide?
I’m a analysis hydrologist, so I concentrate on hydrological impacts of atmospheric rivers. Though they’ll result in flood hazards, atmospheric rivers are additionally important to the Western water provide. Atmospheric rivers have been chargeable for ending more than a third of the area’s main droughts, together with the extreme California drought of 2012-16.
Atmospheric rivers present a mean of 30% to 50% of the West Coast’s annual precipitation.
Additionally they contribute to the snowpack, which supplies a good portion of California’s year-round water provide.
In a mean 12 months, one to 2 excessive atmospheric rivers with snow would be the dominant contributors to the snowpack within the Sierra Nevada. Collectively, atmospheric rivers will contribute about 30% to 40% of a mean season’s whole snow accumulation there.

Justin Sullivan/Getty Images
That’s why my colleagues on the Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes on the Scripps Establishment of Oceanography, a part of the College of California, San Diego, work on improving atmospheric river forecasts and predictions. Water managers want to have the ability to regulate reservoirs and work out how a lot water they’ll save for the dry season whereas nonetheless leaving room within the reservoirs to handle flood danger from future storms.
How is world warming affecting atmospheric rivers?
Hotter air can hold more moisture. As world temperatures rise sooner or later, we are able to anticipate extra intense atmospheric rivers, resulting in an increase in heavy and extreme precipitation events.
My analysis additionally exhibits that extra atmospheric rivers are likely to occur concurrently during already wet conditions. So, the prospect of maximum flooding additionally will increase. One other research, by scientists from the College of Washington, means that there can be a seasonal shift to extra atmospheric rivers earlier within the wet season.
There’ll probably even be extra year-to-year variability within the whole annual precipitation, significantly in California, as a research by my colleagues on the Middle for Western Climate and Water Extremes initiatives.
This text was replace Jan. 31, 2024, with flood alerts and winter storm warnings posted.
[ad_2]
Source link