[ad_1]
In a newly published study, we describe our design for a self-extinguishing rechargeable battery. It replaces probably the most generally used electrolyte, which is very flamable – a medium composed of a lithium salt and an natural solvent – with supplies present in a industrial hearth extinguisher.
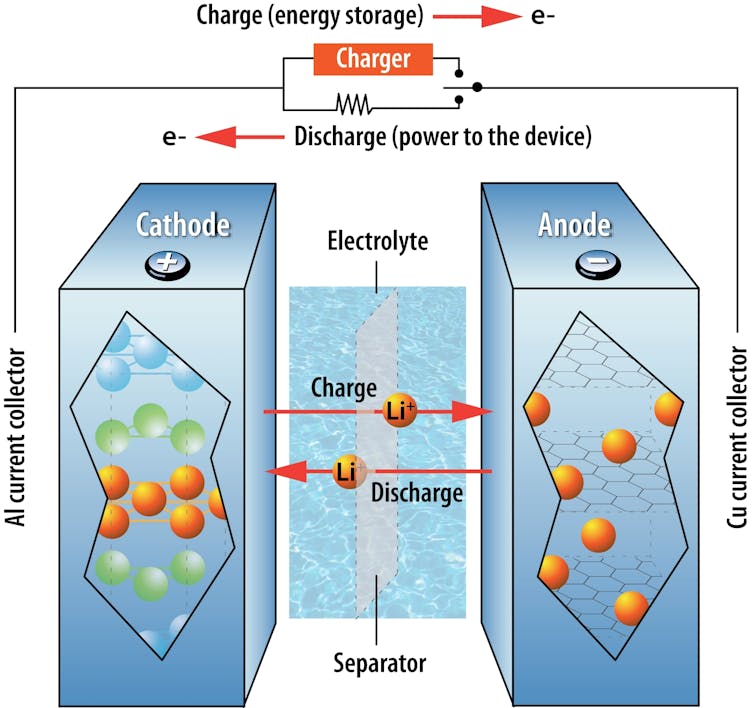
An electrolyte permits lithium ions that carry an electrical cost to maneuver throughout a separator between the constructive and damaging terminals of a lithium-ion battery. By modifying reasonably priced industrial coolants to operate as battery electrolytes, we had been capable of produce a battery that places out its personal hearth.
Our electrolyte labored effectively throughout a large temperature vary, from about minus 100 to 175 levels Fahrenheit (minus 75 to 80 levels Celsius). Batteries that we produced within the lab with this electrolyte transferred warmth away from the battery very effectively, and extinguished inside fires successfully.
We subjected these batteries to the nail penetration check, a typical methodology for assessing lithium-ion battery security. Driving a stainless steel nail through a charged battery simulates an inside brief circuit; if the battery catches hearth, it fails the check. After we drove a nail by way of our charged batteries, they withstood the impression with out catching hearth.
Argonne National Laboratory/Flickr, CC BY-NC-SA
Why it issues
By nature, a battery’s temperature modifications because it expenses and discharges, resulting from internal resistance – opposition throughout the battery to the circulation of lithium ions. High outdoor temperatures or uneven temperatures inside a battery pack critically threaten batteries’ security and sturdiness.
Vitality-dense batteries, such because the lithium-ion variations which can be broadly utilized in electronics and electrical automobiles, comprise an electrolyte formulation dominated by natural molecules which can be extremely flammable. This worsens the chance of thermal runaway – an uncontrollable course of by which extra warmth inside a battery hastens undesirable chemical reactions that launch extra warmth, triggering additional reactions. Temperatures contained in the battery can rise by a whole bunch of levels in a second, causing a fire or explosion.
One other security concern arises when lithium-ion batteries are charged too rapidly. This could trigger chemical reactions that produce very sharp lithium needles referred to as dendrites on the battery’s anode – the electrode with a damaging cost. Finally, the needles penetrate the separator and attain the opposite electrode, short-circuiting the battery internally and resulting in overheating.
As scientists finding out energy generation, storage and conversion, we now have a powerful curiosity in growing energy-dense and protected batteries. Changing flammable electrolytes with a flame-retardant electrolyte has the potential to make lithium-ion batteries safer, and should purchase time for longer-term enhancements that cut back inherent dangers of overheating and thermal runaway.
How we did our work
We wished to develop an electrolyte that was nonflammable, would readily switch warmth away from the battery pack, may operate over a large temperature vary, was very sturdy, and could be appropriate with any battery chemistry. Nonetheless, most identified nonflammable natural solvents comprise fluorine and phosphorus, that are costly and may have harmful effects on the environment.
As an alternative, we centered on adapting reasonably priced industrial coolants that already had been broadly utilized in hearth extinguishers, digital testing and cleansing purposes, in order that they may operate as battery electrolytes.
We centered on a mature, protected and reasonably priced industrial fluid referred to as Novec 7300, which has low toxicity, is nonflammable and doesn’t contribute to international warming. By combining this fluid with a number of different chemical substances that added sturdiness, we had been capable of produce an electrolyte that had the options we sought and would allow a battery to cost and discharge over a full yr with out dropping vital capability.
What nonetheless isn’t identified
As a result of lithium – an alkali steel – is scarce in our Earth’s crust, it is very important examine how effectively batteries that use different, extra considerable alkali steel ions, corresponding to potassium or sodium, fare compared. Because of this, our research centered predominantly on self-extinguishing potassium-ion batteries, though it additionally confirmed that our electrolyte works effectively for making self-extinguishing lithium-ion batteries.
It stays to be seen whether or not our electrolyte can work equally effectively for different forms of batteries which can be in growth, corresponding to sodium-ion, aluminum-ion and zinc-ion batteries. Our aim is to develop sensible, environmentally pleasant, sustainable batteries no matter their ion sort.
For now, nonetheless, since our various electrolyte has comparable bodily properties to presently used electrolytes, it may be readily built-in with present battery manufacturing strains. If the trade embraces it, we count on that firms will be capable of manufacture nonflammable batteries utilizing their present lithium-ion battery amenities.
The Research Brief is a brief tackle attention-grabbing tutorial work.
[ad_2]
Source link

